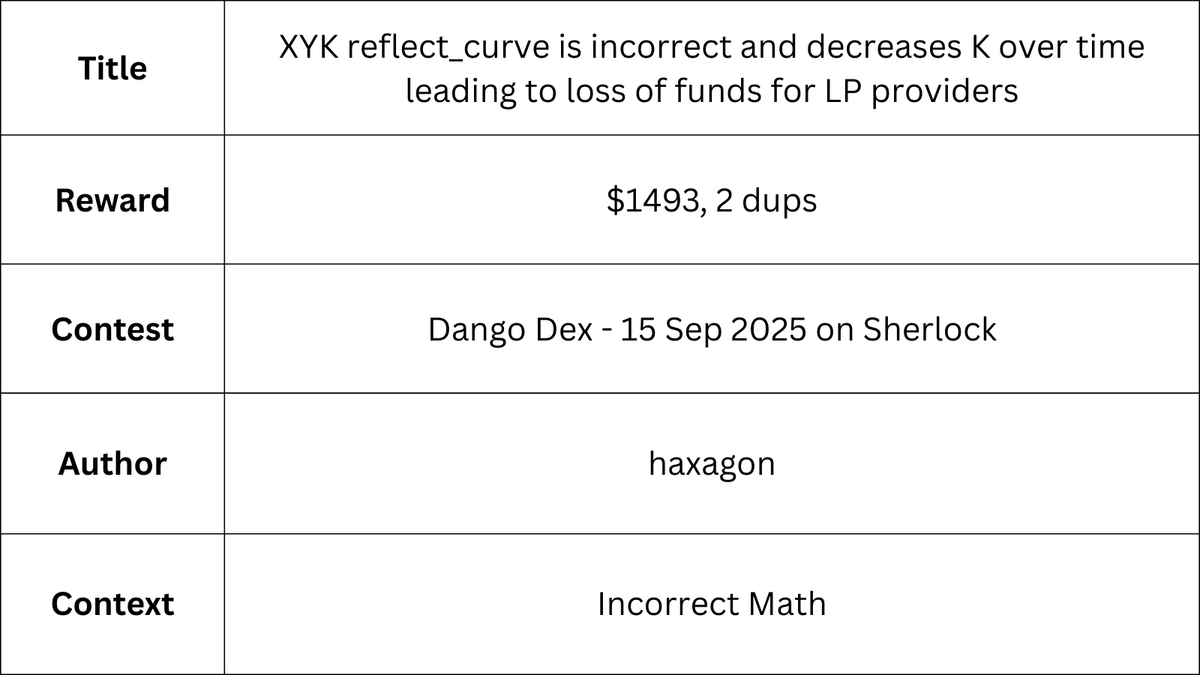
The XYK reflect_curve algorithm that generates passive orders is unfavorable to the pool, computing more unfavorable prices than what the actual AMM algorithm would give.
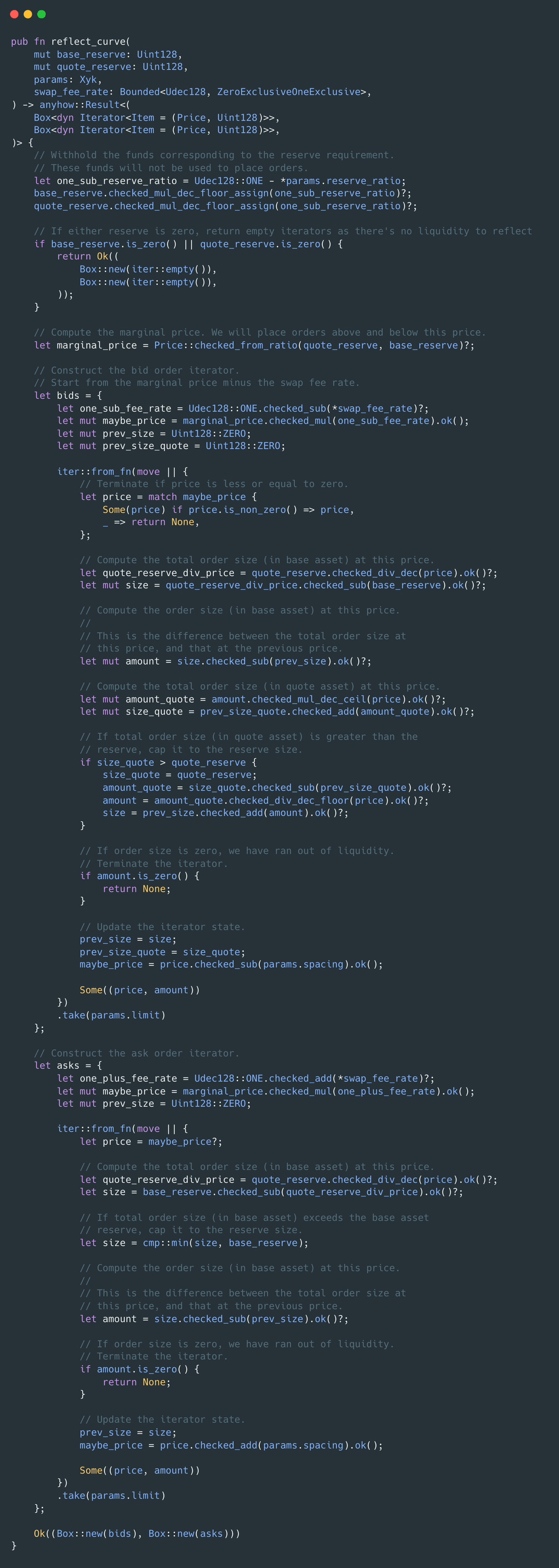
The reason for this is that for instance, for bid orders, the function uses the following to determine the order size at step:
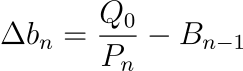
The flaw here is that we are using the initial quote_reserve value Q0 when dividing by price. This assumes that the quote assets do not change as we move away from our initial point of the AMM but in reality it does change. The only thing that does not change should be the K = Q * B. Instead, it should be using the formula:
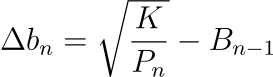
This works because for a given AMM, at the price Pn = Qn / Bn, we can compute the value of Bn in the AMM using:
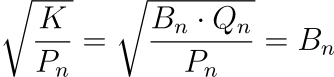
Alpha: this finding can be found by plugging in some numbers and check the output to verify it adds up. For AMMs, the K invariant is supposed to stay the same or increase to provide fees, but in this case it was found out to decrease, so they are losing value. There is a python notebook which helps running some values, otherwise just run some tests.
As such, due to the incorrect pricing, the pool is charging lower than what an regular CP-AMM would charge. This causes the K-invariant to decrease, instead of increase over time causing a loss of funds for LP providers.
Conclusion
This finding would earn you $1493, and the way you would find it is by plugging some numbers to verify that the K increases after pool operations. Additionally, with enough experience intuition would tell you that using a fixed initial price when calculating the delta assets to swap is a red flag.
Full Report
Codebase